Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) or Coronary Heart disease is a serious heart condition that occurs as a result of atherosclerosis. Hardening or narrowing of the artery (stenosis) causes an obstruction in the blood flow to the heart which may lead to major cardiovascular events. When the heart muscle is starved of oxygen, it results in acute chest pain and discomfort (angina) whereas heart attack (myocardial infarction) is the outcome of a completely blocked blood flow through a coronary artery. Hence, it is important to diagnose and treat coronary heart disease as early as possible, as time plays a crucial role here. Plaque build-ups along the inner walls of blood vessels can cause blockage in either single or multiple coronary arteries. Multi vessel disease (MVD) or Multi vessel CAD is the condition where a major epicardial vessel is affected with 70% or greater stenosis and other major vessels are affected with 50% or greater stenosis.
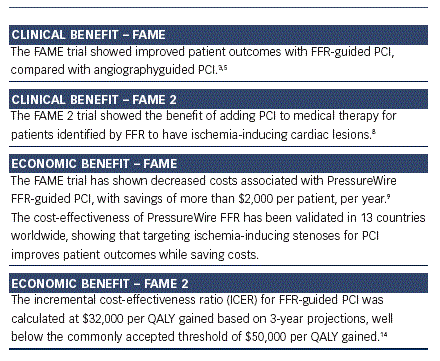
Medical therapy, Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (angioplasty and stenting) and Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) are the treatment options available for coronary heart disease. Interventional cardiologists used to rely on angiography results and other clinical information to detect the evidence of inducible ischemia and guide treatment decisions. Notwithstanding coronary angiography is considered as the gold standard for CAD evaluation, it has been recognised to have several limitations in assessing the functional significance of coronary lesions. In the case of multi vessel coronary disease, the decision-making is far more challenging as angiographic data tend to either overestimate or underestimate the functional severity of stenosis. Revascularization of non-ischemic lesions not only increases the treatment costs but also poses an increased risk for the CAD patient rather than offering any benefit. That is when the results published by the FAME (Fractional Flow Flow Reserve versus Angiography in Multivessel Evaluation) study gained substantial interest in the medical community. It demonstrated that FFR-guided PCI can ensure better outcomes when compared to the angiography-guided PCI.
Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR) measurements can be taken easily during the invasive procedure just before the stenting. A 0.75 cut-off value helps in differentiating between ischemic and non ischemic stenosis. Lesions with a FFR value of less than 0.75 needs drug-eluting stents (DES) while lesions with a FFR value greater than 0.80 should be treated with medical therapy. The FAME study results proved that routine measurements of FFR during PCI significantly reduced the occurrence of myocardial infarction (MI), combined end point of death and repeat revascularization. So it can be hypothesised that FFR measurements are helpful in guiding decisions regarding whether CABG, stenting or medical therapy would be the optimal approach for each CAD patient.








0 comments:
Post a Comment